|
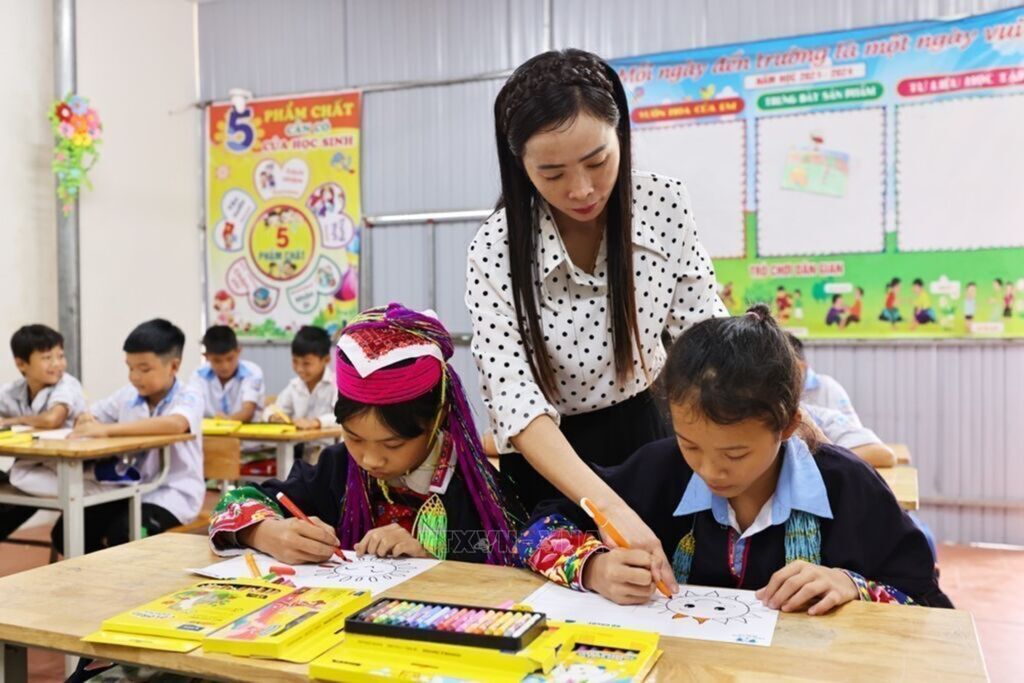
| Teacher Dinh Le Thu guides ethnic minority students during a lesson at Duong Hoa primary school, Duong Hoa commune, Quang Ninh province__Photo: VNA |
Effective as of January 1 next year, the 2025 Law on Teachers (the Law) marks the country’s first standalone legislation that fully outlines the legal status, rights and obligations of, and policies toward, teachers.
With 42 articles arranged in nine chapters, the Law affirms the legal status and protects the reputation, honor and dignity of teachers, sets out professional ethical standards, provides preferential policies to increase teachers’ salary and income, standardizes teachers’ qualifications, and gives the education sector greater autonomy in recruitment and employment of teachers.
Legal status, reputation, honor and dignity of teachers
For the first time, the Law establishes a comprehensive legal status for teachers working in both public and non-public education institutions. It affirms that teachers play a decisive role in ensuring the quality of education, and a key role in developing human resources and building a learning society and an advanced culture deeply imbued with national identity.
Teachers are regarded as “special public employees” and “special workers” who are entitled to professional rights relevant to their status, including the right to be respected, protected and honored.
Noteworthily, the Law provides mechanisms to protect teachers from acts offending their reputation, honor and dignity, especially the act of spreading information that blames teachers for any school mishaps without official conclusions made by competent agencies. Depending on the nature and severity of their violations, violators will be subject to disciplinary action, administrative sanctioning or examination for penal liability. Violations committed within the premises of education institutions or while teachers are performing professional activities will be strictly handled in accordance with law.
Alongside the right to be protected, teachers also bear the responsibility of upholding professional ethics. The ethical standards are incorporated in the Law with specific codes of conduct governing teachers’ interactions with students, colleagues, students’ families, and the community. The Law affirms that the responsibility to lead by example is an inseparable part of the teaching profession, reflected in teachers’ integrity, exemplary behavior and dedication in both teaching activities and social behaviors.
Preferential salary and remuneration policies for teachers
The Law stipulates that teachers’ salaries will be ranked highest in the administrative and non-business salary scale. In addition, teachers will be entitled to profession-based preferential allowance and other allowances based on the nature of jobs and geographical areas where their schools are located.
The Law also provides policies to attract talented individuals into the education sector, encourage skilled professionals in important sectors to become teachers, encourage teachers to work in disadvantaged regions, ensure more equitable quality across regions, and retain experienced teachers in the sector.
Accordingly, all teachers working in both public and non-public education institutions will be entitled to subsidies, support for training and further training, regular health checks and occupational health care, access to official housing and support for payment of travel expenses if working in localities with extremely difficult conditions.
Preferential treatment policies will also be provided for teachers with high qualifications, exceptional talent, special aptitudes or advanced professional skills, as well as those working in extremely difficult areas or in essential or critical fields.
Teachers in early childhood education institutions may, if they wish, retire at an age lower than the retirement age of workers under normal conditions, provided the early retirement period does not exceed 5 years. If they have paid social insurance premiums for full 15 years or more, the percentage of their pension benefits will not be reduced because of early retirement. Meanwhile, teachers holding the title of professor or associate professor or possessing a doctoral degree, and those working in specialized fields or sectors, are eligible for late retirement.
Standardizing and improving teachers’ quality
For each teacher title, the Law provides teachers’ professional standards which will be applied uniformly to teachers in public education institutions and non-public education institutions. As defined in the Law, teachers’ professional standards are applicable to different teacher titles and include the standard on teachers’ ethics, the standard on training and further training levels, and standard on professional capacity and skills.
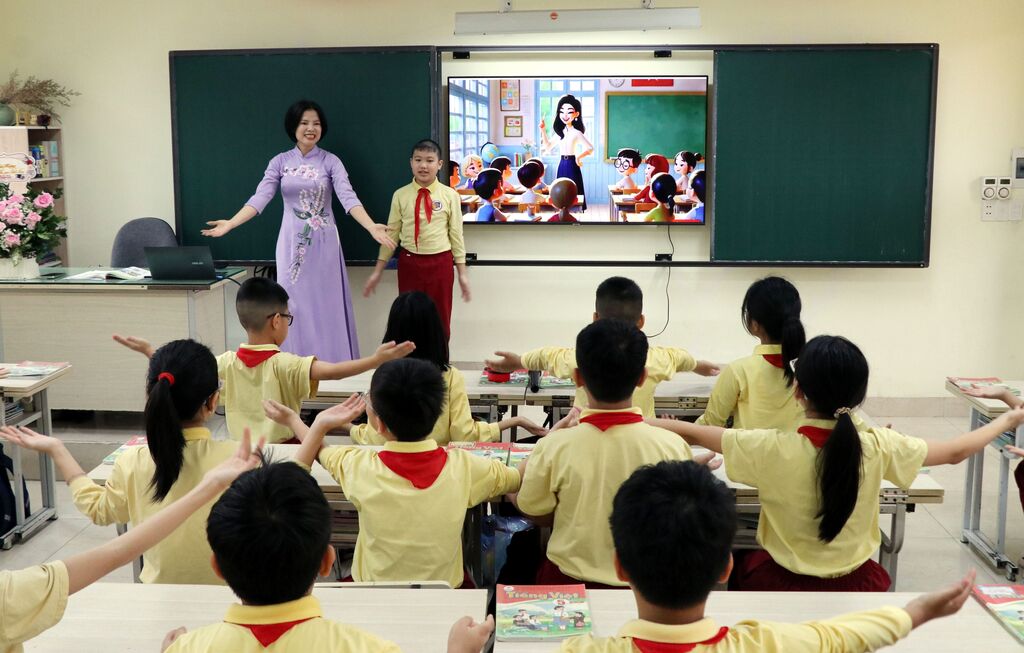 |
| Teacher Pham Thi Hoa uses digital teaching equipment during a lesson at Pham Hong Thai primary school, Nam Dinh ward, Ninh Binh province__Photo: VNA |
The recruitment of teachers will be carried out in the form of examination and selection, in which pedagogical practice is a mandatory requirement. This aims to ensure the selection of candidates who meet professional competency standards appropriate to each educational level and training qualification.
The policies on secondment, transfer and assignment of teachers for inter-school and inter-level teaching in public education institutions are comprehensively provided as a basis for assigning teachers in conformity with their professional duties and the needs of the education sector.
Empowering the education sector
Under the Law, the Government will perform the unified state management of teachers while the Ministry of Education and Training (MOET) will act as the focal point responsible to the Government for performing the state management of teachers. The MOET will take charge of, and coordinate with related ministries, ministerial-level agencies and provincial-level People’s Committees in, formulating strategies, schemes and plans for development of teachers. The MOET is also empowered to determine total payrolls of teachers under its management before submitting them to competent authorities for approval.
The Law empowers heads of education institutions to recruit teachers depending on their needs. For schools of the people’s armed forces, the competence to recruit teachers must comply with the regulations of the Minister of National Defense or the Minister of Public Security.
Empowering the education sector in the recruitment and employment of teachers aims at removing longstanding bottlenecks, particularly the persistent imbalance between teacher shortages and surpluses, and enabling proactive formulation of short-, medium- and long-term plans on development of the teachers’ pool.- (VLLF)